Enterprise applications for business hold a ton of value, from boosting productivity to delivering critical data-driven insights, but with so many of them flooding the market, it’s hard to pick the one that best serves your unique business needs. AI integrations, low-code, no-code, expert customizations, add-ons – just so many functionalities to look at.
Selecting enterprise applications for business isn’t just about matching the right features. It also warrants an in-depth sync with your immediate and distant business strategy, budget, scalability, and user adoption goals. Plus, avoiding the common pitfalls is just as important. After all, the popular one in the market may not be the best.
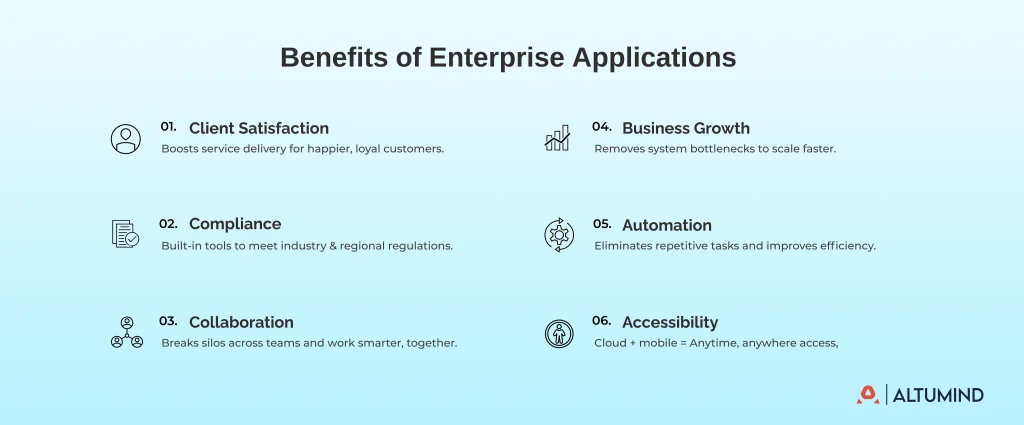
So, which one is, and how do we arrive at that solution? Let’s explore
Enterprise Applications for Business: Key Factors to Consider
1. Scalability and Flexibility:
Increasing workloads from business growth demand applications that support seamless scalability without latency. High user count, data volume, more processes, and throughput can destabilize the system and compromise operational integrity, affecting business continuity. The underlying architecture must support load balancing, API Scalability, resource optimization, microservices/containerization, horizontal and vertical scaling, and elasticity of cloud-based models in high-stress peak usage for better fault tolerance and improved response times.
2. Security:
The enterprise app would need a real-time, proactive incident response system to isolate threats and protect against data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. Both data at rest and in transit will need 24/7 surveillance for manipulation and/or deletion.
The solution must feature end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), audit trails and logging, and use ML and AI-driven threat analysis to detect anomalies, prevent unauthorized sharing, and predict potential attacks.
3. Integration and Interoperability:
Connecting with disparate 3rd-Party systems for real-time data exchange requires the enterprise applications to have a diverse, deep, and future-ready integration framework. This ensures compatibility with legacy systems, lowers silos, and allows them to onboard emerging systems/partners and facilitate innovation without significant disruptions. Look for applications with open API frameworks, pre-built connectors of popular platforms, strong middleware support, real-time data synchronization, and data transformation tools.
4. Customization:
Enterprise applications for business must also offer heightened customization. Get the application to adapt to their unique workflows and pain points. Personalization empowers organizations to tailor their interface, processes, and functionalities to their distinct departmental strategy, allowing flexibility at the configuration and development levels, while minimizing technical debt and maintaining compatibility. Look for role-based dashboards, custom reporting, configurable workflows, multi-lingual support, API customization, and version control in sandbox environments.
5. Cost:
For financial stability and maximum value, Software development costs is another parameter that organizations could evaluate when selecting an enterprise application, be it budget allocation, return on investment (ROI), and total cost of ownership (TCO), such as upfront and ongoing costs.
Organizations must study the pricing model in detail – upfront licensing, subscription fees, usage fees, maintenance, and customization expenses. Further, evaluate free trials, bundled offers, pay-as-you-go options, cost optimization tools, and finally, the ability to upgrade/downgrade a plan.
6. Vendor Support and Documentation:
At some point, businesses will run into issues, which is when support becomes critical. A strong, well-structured content repository of FAQs, backend manuals, and forum support to configure and test changes, or an L1, L2, and L3-assisted multi-channel customer support desk to escalate issues for timely resolution.
Businesses can look for live chat, email, and phone support, service-level agreements (SLAs), interactive tutorials, webinars, communication on new features and fixes, step-by-step guides, and a dedicated account manager.
7. Performance:
Performance is non-negotiable, another key factor to consider while evaluating enterprise applications for business. Top-tier speed, resulting in fast response time under stressful environments, is crucial to prevent downtime and ensure operational efficiency. The idea is to get robust performance during peak hours under dynamic business conditions.
Any application that provides caching and data optimization, throttling controls, performance monitoring dashboards, built-in redundancy, and high concurrency (multiple users/services) support is best for your business.
8. Analytics and Reporting:
Modern enterprise applications offer analytics and reporting to deep dive into intricate, meaningful, and real-time data. All leads to actionable intelligence, helping uncover trends and identify bottlenecks.
Modern applications must include more than just basic reporting, leaning towards dynamic insights and granular analytics from raw data. What makes it possible? It’s the self-service BI, multi-source data integration, drill-down reporting, predictive AI/ML analytics, intuitive dashboards, and much more.
9. User Experience and Accessibility:
A well-designed UX in enterprise applications for business affects employee satisfaction, which then affects user adoption rates and operational efficiency. A seamless UX/UI interface minimizes friction, improves collaboration, eases onboarding, and streamlines workflows. Adaptive interfaces, intuitive dashboards, mobile responsiveness, self-service portals, and AI-driven user assistance make it come true. These elements collectively optimize the enterprise application for efficiency and engagement.
10. Implementation Complexity & Timeline:
The implementation complexity is another factor to look out for, as it directly impacts business continuity and user adoption. A meticulous execution can lead to delays and cost overruns. It’ll come down to existing systems integration, data migration, and other key factors.
This matters because a lengthy and complicated implementation can affect downtime, improved user engagement, and seamless workflow automation. Look for pre-configured templates, API-driven integration, modular architecture, and other key features. If implementing one feels cumbersome or you lack access to reliable and certified experts who can handle such a large-scale deployment, Altumind can help.
Examples of Enterprise Software Applications
1. Logistics and Supply Chain:
Plan, execute, and monitor logistics and get real-time visibility across inventory, demand forecasting, and order fulfillment. Integrate with procurement and warehousing systems to improve your supply chain flexibility across global networks. Two examples of enterprise software applications in logistics are SAP SCM (Supply Chain Management) and Oracle Transportation Management.
2. Human Resources:
Access talent management, payroll, and workforce analytics from a single centralized interface. Support every aspect of employee lifecycle management and automate the cumbersome HR processes with SAP SuccessFactors and Workday HCM.
3. Sales:
Manage every aspect of the lead pipeline end-to-end. From sourcing to tracking and closure, view granular insights about clients in rich detail. The intuitive UX and in-depth analytics let you unlock more opportunities. Two premier examples of enterprise software applications in sales are Salesforce Sales Cloud or HubSpot Sales Hub (Enterprise).
4. Finance & Accounting:
Automates financial functions like general ledger, billing, and compliance management, plus extends real-time visibility into financial performance and leverages predictive analytics for strategic planning. Oracle NetSuite ERP or SAP S/4HANA Finance are two reliable enterprise solutions in this space.
5. Customer Support & Service:
Manage phone, email, and chat all on one platform. End-to-end workflow automation with the support of AI-powered chatbots, ticketing levels, and robust reporting for faster issue resolution and better service experiences. Zendesk Enterprise Suite and ServiceNow Customer Service Management are 2 customer support enterprise applications in this function.
Concluding Enterprise Applications for Business
Selecting the right enterprise business application is a strategic decision that can dictate how your business creates efficiency and grows from here. From performance to user experience and a plethora of integrations, businesses need an application that ties with their unique needs. With cloud-native, API-first, and modular platforms, businesses can have the flexibility to build systems that adapt to changing demands.
At Altumind, we know every enterprise has its challenges and priorities. That’s why we don’t believe in a generic solution. We identify the current state, identify gaps, and implement solutions that deliver immediate value and future-proof scalability. Whether you’re modernizing a legacy system or building from the ground up, having the right partner can make a world of difference.
Need help choosing or implementing the right enterprise app? Altumind is here to make it seamless.


